
When the clock is ticking in time-bound, customer-sensitive operations, using Lean Six Sigma can be a smart move toward achieving operational excellence and customer satisfaction. In this case study, one large insurance company executed a Lean Six Sigma project to cut operational costs for property and casualty (P&C) insurance claims and improve customer satisfaction. The project was completed in the medical bill review process for personal injury protection (PIP) and medical payment (med pay) auto insurance coverage. PIP and med pay are part of the auto insurance coverage that pays for medical expenses, funeral expenses, and, in some cases, lost wages and other damages resulting from an automobile accident for the insured customers and others riding in a car or walking.
Define
The insurance company outsourced its PIP and med pay bill review process to a leading medical bill review company. The medical bill review process was laden with repetitive and inefficient handoffs between the insurance company and its outsourcing partner, which led to loss of money and time. Delays in the bill review process also caused customer dissatisfaction, which manifested in a high volume of inbound phone calls as customers and medical providers sought to understand the status of bill payment. Also, delays beyond 30 days in the medical bill review process lead to payment of interest, fines and penalties, as there are 30 states (within the United States) that have legal regulation for a bill review cycle time of 30 days.
The goal of the project was to reduce the average cycle time of the PIP and med pay bill review process from 28 days to 15 days. The targeted benefit was an annual cost saving of $1 million, based on savings in partner bill review expenses, adjusting expenses, loss cost, cost of law suit avoidance and cost of non-value-added activities.
Measure
In order to measure improvement, the team defined the key output metric for the PIP and med pay bill review process (Table 1).
Table 1: Operational Definition of Output Metric
| Key Output Metric | Definition | Measurement Unit | Specification Limits |
| Process cycle time | Elapsed time between start of bill review process until decision | Days | Upper (USL) = 30 days for 30 selected states, Lower (LSL) = 0 days |
They also created an as-is map of the process (Figure 1).
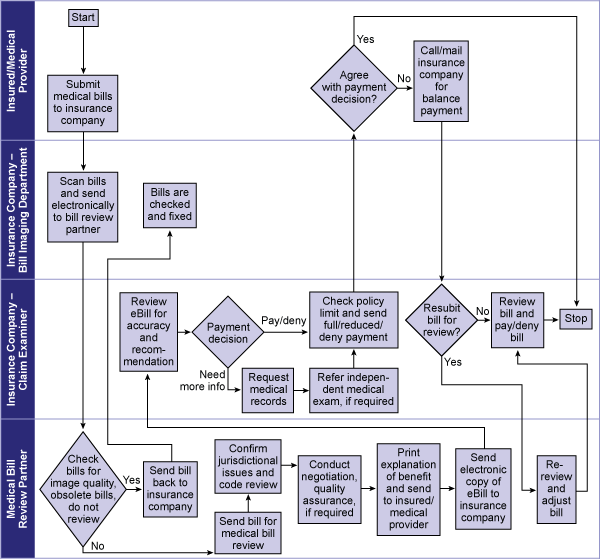
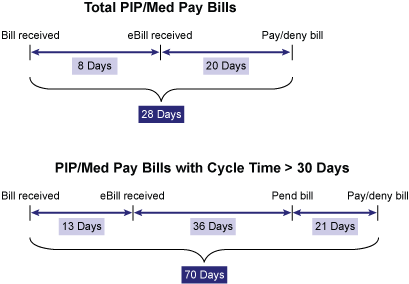
There are 30 states that require a 30-day-or-less bill review cycle time. Figure 2 shows that on average, bill review cycle time is 28 days for all states. For states where there is no legal requirement of 30 days, bill review cycle time is 70 days.
Analyze
The team created a fishbone diagram to outline potential causes for bill review cycle time greater than 30 days related to the machines, methodology, providers, measurements, partner operations and internal operations involved.
They also conducted hypothesis testing, which confirmed that the 30-day bill review response time requirement does impact actual turnaround time (Figure 3).
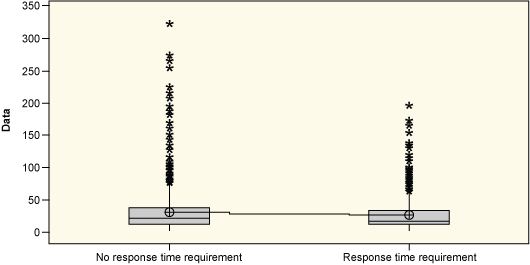
Two-sample T-test for states with no response-time requirement vs. states with response-time requirement
| N | Mean | StDev | SE Mean | |
| No response-time requirement | 1000 | 31.6 | 33.9 | 1.1 |
| Response-time requirement | 987 | 27.3 | 25.4 | 0.81 |
Difference = mu (No response-time requirement) – mu (Response time requirement)
Estimate for difference: 4.22571
95% CI for different (1.592888, 6.855853)
T-test of difference = 0 (vs not =). T-value = 3.15 P-value = 0.002 DF = 1853
Conclusion: 30-day response-time requirement does impact bill review cycle time.
Improve
Next, the team conducted process value analysis to identify the non-value-added activities contributing to delays in the bill review process (Table 2).
Table 2: Wasteful Activities and Solutions
| Non-value-added Activities | Solution Snapshot | Projected Savings |
| Redundant partner review of bills – Certain bills were denied for payment due to unreasonable, unrelated and unnecessary causes at the end of the bill review of process | Bills should come to the examiner first to check policy limits, coverage, deductible, relatedness and need for medical records, and then be emailed to the bill review partner for further review. Adjuster should provide reasons for overridingand fees for such bills should not be paid to bill review partner. | $50,000 |
| Re-review of bills due to lack of information | Medical provider should pay the processing fee for errors in the bill. They should also be charged for medical records request fees for not sending medical records along with bills for those states where medical records are mandated. | $230,000 |
| Untimely payment, denial of bills due to lack of metrics for turnaround time | Track compliance of partners and insurance company with bill review cycle time service-level agreement. USL for bill review cycle time needs to be set to 30 days for all states. Twenty-one days should be set as the target for average bill review cycle time. | $47,000 |
| Inconsistencies in bill review for same medical treatment at a given time at the same physical location | Identify medical treatment codes where the variation is observed. Complete a gage R&R check for medical bill review regularly tp rectify inconsistencies in partner medical bill review process. Add reward/penalty clauses in the partner’s contract for handling inconsistencies in partner’s recommendations that lead to lawsuits. | $330,000 |
| Bill review summary called explanation of benefits (EOB) and payment check sent are separately, leading to confusion and calls from medical providers and customers. | Automatic payment – EOB and check printed in house within insurance company. | $129,000 |
| EOB unnecessarily sent for bills paid in full. Effort spent on unnecessary tasks leads to loss of bill review throughput capacity. | Printing and mailing EOB to be stopped for bills paid in full. | $40,000 |
| Partner unnecessarily reviewing bills from non-partner bill review states: MD, AL, LA, MO, MS, OK, TN | Proper communication mechanism to be established between unit managers, imaging and scanning area and medical management team on a standard frequency regarding the states that will not send bills to partner. | $30,000 |
| Paying flat bill review fees per bill | Contract to be revised with partner to pay bill review fees per line item instead. | $340,000 |
| Grand total: | $1.619M |
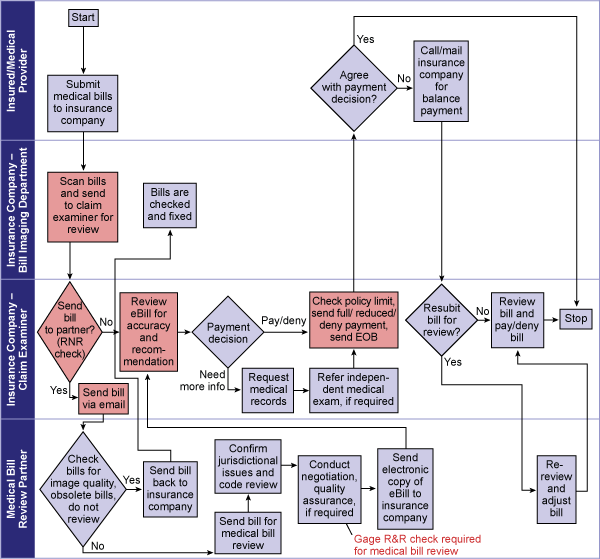
Figure 4 shows the PIP and med pay bill review to-be process (process steps marked in red are the changes to as-is process).
Control
The team tested the new process with pilots in a few states initially, and rolled out a detailed control plan to all states after the success of the pilot.
Bill review cycle time was reduced from 28 days to 15 days by controlling the items causing variation and delays. This helped the company avoid paying $1.6 million in interest, penalties, fines and law suit fees.