
Problems and defects are expensive. Customers understandably place high expectations on manufacturers and service providers to deliver quality and reliability.
Often, faults in products and services are detected through extensive testing and predictive modeling in the later stages of development. However, finding a problem at this point in the cycle can add significant costs and delays to schedules. The challenge is to design with quality and reliability at the beginning of the process and ensure that defects never arise in the first place.
One way that Lean Six Sigma practitioners can achieve this is to use failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA). This is one of the best tools for identifying potential problems and their impact.
FMEA: The Basics
FMEA is a qualitative and systematic tool. You’ll usually create it within a spreadsheet. This helps practitioners anticipate what might go wrong with a product or process. Using this tool shows how a product or process might fail and the effects of that failure. FMEA also helps find the possible causes of failures and the likelihood of failures being detected before occurrence.
FMEA is one of the best ways of analyzing potential reliability problems early in the development cycle. In turn, it makes it easier for manufacturers to take quick action and mitigate failure. The ability to anticipate issues early allows practitioners to design out failures and design for reliable, safe, and customer-pleasing features.
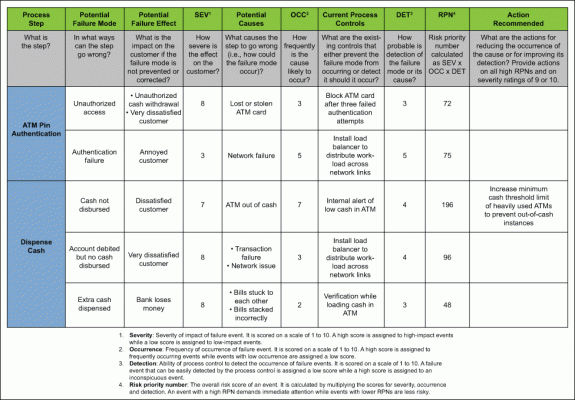
Finding Failure Modes
One of the first steps to take when completing an FMEA is to determine the participants. You need the right people with the right experience. This could include process owners and designers. All qualified personnel should be involved to catch potential failure modes. Practitioners also should consider inviting customers and suppliers to gather alternative viewpoints.
Once the participants are together, the brainstorming can begin. When completing an FMEA, it’s important to remember Murphy’s Law: “Anything that can go wrong, will go wrong.” Participants need to identify all the components, systems, processes, and functions. Any of these factors could potentially fail to meet the required level of quality or reliability. The team should not only be able to describe the effects of the failure but also the possible causes.
Table 1: FMEA for Car Tire
| Function or Process Step | Failure Type | Potential Impact | SEV | Potential Causes | OCC | Detection Mode | DET | RPN |
| How severe is the effect on the customer? | Describe what has gone wrong | What is the impact on the key output variables or internal requirements? | How severe is the effect on the customer? | What causes the key input to go wrong? | How frequently is this likely to occur? | What are the existing controls that either prevent the failure from occurring or detect it should it occur? | How easy is it to detect? | Risk priority number |
| Tire function: support weight of car, traction, comfort | Flat tire | Stops car journey, driver and passengers stranded | 10 | Puncture | 2 | Tire checks before journey. While driving, the steering pulls to one side, and excess noise | 3 | 60 |
| Recommended Actions | Responsibility | Target Date | Action Taken | SEV | OCC | DET | RPN |
| What are the actions for reducing the occurrence of the cause or improving the detection? | Who is responsible for the recommended action? | What is the target date for the recommended action? | What were the actions implemented? Now recalculate the RPN to see if the action has reduced the risk. | ||||
| Spare tire and appropriate tools permanently carried in the trunk | Car owner | From immediate effect | Spare tire and appropriate tools permanently carried in the trunk | 4 | 2 | 3 | 24 |
Criteria for Analysis
An FMEA uses three criteria to assess a problem: 1) the severity of the effect on the customer, 2) how frequently the problem is likely to occur, and 3) how easily the problem can be detected. Participants must set and agree on a ranking between 1 and 10 (1 = low, 10 = high) for the severity, occurrence, and detection level for each of the failure modes. Although FMEA is a qualitative process, it is important to use data (if available) to qualify the decisions the team makes regarding these ratings. A further explanation of the ratings is shown in Table 2.
Table 2: FMEA Severity, Occurrence, and Detection Ratings
| Description | Low Number | High Number | |
| Severity | Rank the probability of a failure occurring during the expected lifetime of the product or service | Low impact | High impact |
| Rank the probability of a failure occurring during the expected lifetime of the product or service | Rank the probability of a failure occurring during the expected lifetime of the product or service | Not likely to occur | Inevitable |
| Detection | Rank the probability of the problem being detected and acted upon before it has happened | Very likely to be detected | Not likely to be detected |
After ranking the severity, occurrence, and detection levels for each failure mode, the team will be able to calculate a risk priority number (RPN). The formula for the RPN is:
RPN = severity x occurrence x detection
In the FMEA in Figure 1, for example, a flat tire severely affects the customer driving the car (rating of 10), but has a low level of occurrence (2) and can be detected fairly easily (3). Therefore, the RPN for this failure mode is 10 x 2 x 3 = 60.
Setting FMEA Priorities
Once all the failure modes have been assessed, the team should adjust the FMEA to list failures in descending RPN order. This highlights the areas where corrective actions can be focused. If resources are limited, practitioners must set priorities on the biggest problems first.
There is no definitive RPN threshold to decide which areas should receive the most attention. This depends on many factors, including industry standards, legal or safety requirements, and quality control. However, a starting point for prioritization is to apply the Pareto rule: typically, 80 percent of issues are caused by 20 percent of the potential problems. As a rule of thumb, teams can focus their attention on failures with the top 20 percent of the highest RPN scores.
Making FMEA Corrective Actions
When the priorities have been agreed upon, one of the team’s last steps is to generate appropriate corrective actions for reducing the occurrence of failure modes, or at least for improving their detection. The FMEA leader should assign responsibility for these actions and set target completion dates.
Once corrective actions have been completed, the team should meet again to reassess and rescore the severity, probability of occurrence, and likelihood of detection for the top failure modes. This will enable them to determine the effectiveness of the corrective actions taken. These assessments may be helpful in case the team decides that it needs to enact new corrective actions.
The FMEA is a valuable tool that can be used to realize several benefits. This includes improved reliability of products and services, prevention of costly late design changes, and increased customer satisfaction.
Real-World Uses of FMEA
Typically, this tool is used in the context of software development. However, its principles can be applied across the board to other industries. Consider the application of FMEA for food products. There is no shortage of failure states and defects with food. As such, there is a potential for catastrophe to occur.
A manufacturer would have to consider the following while packaging lunch meat:
| Process Step | Failure Type | Potential Impact | SEV | Potential Causes | OCC | Detection Controls | DET | RPN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging of Luncheon Meat | Contamination | Customers get sick, possibly deaths | 9 | Workers getting PPE contaminated during the handling of materials | 3 | All workers are required to swap out PPE when moving between stations | 2 | 54 |
As you can see in the above figure, the failure type can have horrible results. It makes sense that detection controls are in place to reduce the risk of contamination between workstations. Ideally, the food manufacturer has strict detection controls in place.
Other Useful Tools for Detecting Failures and Faults
Catching defects before they happen minimizes time and costs that can be better used elsewhere. Taking the time and energy to invest in the four pillars of quality can yield fantastic results. This sort of planning allows you to account for the VOC and maintain reliable deliverables in one fell swoop.
Additionally, using an Ishikawa Diagram and the 5Ws can go a long way toward finding issues in your production workflow. These tools are intended for root-cause analysis and go hand-in-hand with the likes of FMEA toward improving your deliverables and saving costs.
Real-World Uses of FMEA
FMEA sees applications across a wide selection of industries. A recent example would be in use the petroleum industry where FMEA is used to design safe and effective subsea control systems. With so much of the petroleum industry moving off-shore, this is a vital way of guaranteeing the safety of not just the rig, but of employees and the pipeline as well.
Further, it’s seeing use in the evaluation of other vital structures like dams. This past summer saw the use of the modified fuzzy FMEA methodology to assess the risk involved with the construction of Eyvashan Dam. This use of FMEA isn’t just looking at the risk involved for people, but the ecological damage in the event of a system failure.