
© Tint Media/Shutterstock.com
Key Points
- Red X is a method for checking dominant causes in variation.
- Red X uses a similar approach to DMAIC but is created solely for the approach.
- The approach can be readily used to reduce defects and improve the process as a whole.
The fundamental premise of the Shainin Red X® process is that for any problem, there is a dominant root cause that must be eliminated or mitigated for the process to be improved. In this article, we will define the Red X process, best practices, and how it can be applied to your organization.
What is Red X?
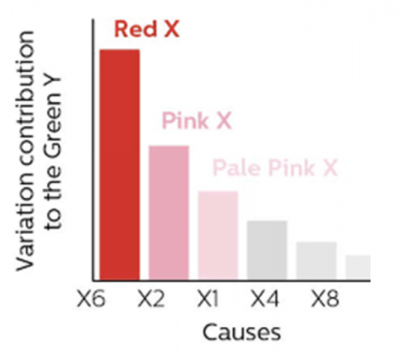
The Red X method is based on the key assumption there is always a dominant cause of variation. This statement is based on the application of the Pareto principle to the causes of the variation. Generally, the variation of the output is caused by the variation of several inputs. These inputs (Xs) are categorized by color, with the Red X being the dominant root cause. Shainin defines the desired state of the output as the GreenY®.
Instead of the DMAIC methodology of Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control, the Red X approach uses the following structure, called FACTUAL:
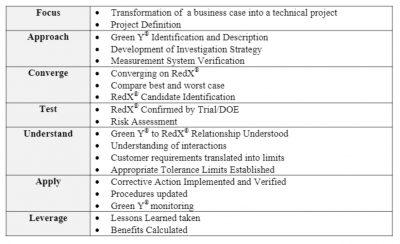
Shainin Red X FACTUAL approach to problem-solving
Red X vs. DMAIC
While we’ve explored a bit of this approach, it is important to compare it to the common DMAIC used in Six Sigma. While DMAIC can be useful for process improvement, it doesn’t take the same approach as Red X. Red X is evidence-based, utilizing hard data to analyze the problem. DMAIC can do so, but that isn’t the primary aim of the methodology.
An Industry Example of Red X
The problem was Post Burning Blow Holes on automotive batteries. The post burner is an automatic burning machine designed to weld the cylindrical bushing of an automotive battery to a specified depth of burn. If blow holes are seen on the battery post, then the battery is rejected.
Shainin Red X techniques were used to reduce the percentage of reworks from 0.15% to 0.03%. DOE was used as the primary tool along with:
- Multivariate analysis
- Variable search
- Paired comparison
- Component Search
- Product/process search
- Scatter plots
Best Practices for Red X
Here are a few tips on using Red X in your organization.
Understanding the Process
You must have a deep understanding of the Y and the problem.
Problem-Solving
The Red X approach is very diagnostic. It is the identification, analysis, and quick zooming in on the root cause.
MSA
You must have confidence in the quality of the data captured by your measurement system. This requires you to do an MSA study to validate your data.
Other Useful Tools and Concepts
Learning to adapt to defects is one of the core things you can learn in any production environment. As such, learning how to create a corrective action report is one of the most useful documents you have at your disposal.
Additionally, if you’re new to Six Sigma, why not learn how it applies across different definitions? This isn’t just a management approach or methodology, but a fully comprehensive term encompassing multiple contexts.
Conclusion
Red X is a problem-solving technique based on the premise there is one dominant root cause for process variation and problems. Using a convergent process of analysis focusing on potential process input variables (X), the result will be an identification of the primary Red X root cause along with lesser colors of Pink Xs.
The image featured at the top of this post is ©Tint Media/Shutterstock.com.