Lean Six Sigma is a set of tools used to improve organizational processes. One tool, DMAIC, improves existing processes. Define-Measure-Analyze-Design-Validate/Verify (DMADV) is a tool for designing new processes or improving processes that are too broken to fix.
This article will focus on how DMADV is used, its benefits and best practices, and an example of how it can be applied.
What is DMADV?
According to iSixSigma.com, DMAIC is a data-driven process-improvement methodology that focuses on properly identifying the problem, utilizing data to determine the root cause, developing and implementing the solution, and verifying that the solution continues to be effective over time.
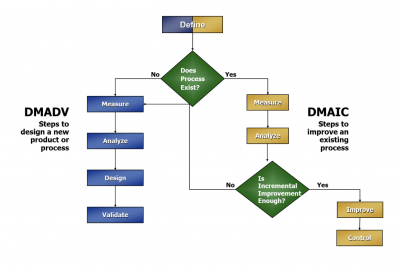
DMAIC is an acronym that stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It improves existing processes either incrementally or breakthrough.
But, what if the existing process can’t be improved enough to meet expectations? Or, if you need to design a new process? Then, DMADV is the tool of choice.
The graphic below shows the steps of the DMADV process.
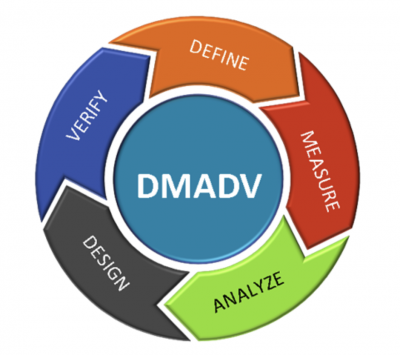
DMADV is a Design For Six Sigma (DFSS) method that focuses on customers. The DMADV (Define-Measure-Analyze-Design-Validate/Verify) method aims to design a new process or product or to redesign a problematic process or product.
The approach initially follows the first three steps of DMAIC and then shifts to a different perspective in the Design/Redesign and Validate/Verify steps to achieve improvement.
Let’s explore the DMADV steps in more detail.
Define
The goals here are to identify the purpose of the project and identify and set realistic and measurable goals based on the expectations of your customer, organization, and stakeholder(s). A clear definition of the project is set, and every strategy and goal aligns with the expectations of the organization and customers.
Measurement
This step defines the factors that are critical to quality (CTQs). These need to be quantified and data collected.
Analyze
In this step, you will:
- Develop design alternatives
- Identify the optimal combination of requirements to achieve value within any constraints
- Develop conceptual designs
- Evaluate them
- Select the best elements
- Develop alternatives for your design
Design
This step includes both a detailed and high-level design for the selected alternative. The elements of the design are prioritized, and from there, a high-level design is developed. Then, a more detailed model can identify where errors may occur and make necessary modifications.
Verify
In this final step, the team validates and verifies whether the design is acceptable to all stakeholders. Is the design realistic? You may need to pilot the design and try some production runs to be sure the quality will meet expectations.
Lessons learned are documented. You will also include a plan to transition the product or service to the process or product owner and develop a control plan to sustain the change.
The graphic below compares DMAIC with DMADV.
Benefits of DMADV
As a structured methodology for improvement, DMADV has several benefits.
Customer Driven
DMAIC starts with the existing process or product and seeks to make an incremental change. DMADV starts with customer expectations and requirements and designs a new process or product to meet those.
Structured
The DMADV methodology is a sequential, structured set of activities and deliverables to allow a team to stay focused and on task.
Synergy
In addition to the members of a DMADV project team, many other parts of the organization are engaged in this process since consideration must be given to people, manufacturing, raw materials, engineering, and IT issues so that the final design is optimized for your organization.
Why Is DMADV Important to Understand?
DMADV can be an intense process to execute. By understanding how it works, you will be able to complete your DMADV project without any serious problems.
Used for New Processes
You can use DMAIC to improve existing processes. If you want or need to start with a fresh design, then the initial focus will be on the customer.
Requires an Interactive Approach to Design
The process starts with a series of alternative designs before going to a preferred high-level design, and then cascading down to detailed designs and their components.
Prototyping Is Important
It is important to understand that you don’t jump from final design to execution. There are many unknowns in your new design, so it will be helpful to utilize prototypes and Design of Experiments (DOE) to confirm everything.
An Industry Example

A company based in Germany produces and sells bicycles to a global marketplace. They had recently expanded production to the U.K. as well as Italy. Unfortunately, they started to experience some supply chain problems.
The decision was made to see if their current process can be redesigned to meet customer requirements using DMADV. In this case, the customer was the leadership team since this was an internal issue. Here are some highlights of their project.
Define
The goal was to redirect 100% of outsourced products from outside vendors to the U.K. and Italy. The project team consisted of team members from production, logistics, engineering, supply chain, and legal.
Measure
CTQs were identified based on leadership input. A current state, as-is process map was drawn. All suppliers and their products that were in scope were identified. Data was collected on delivery and inventory issues.
Analyze
The team decided to focus on common parts based on volumes following the Pareto principle. The legal department contacted all suppliers and explained the new expectations for the shipping of bike components.
Design
A new process was designed to consider the following:
- New contracts with component suppliers
- The supply chain calculated new expected order volumes
- Component prices were reviewed and repriced
- Logistics needed to contact transportation companies and negotiate prices, delivery times, and overall expectations
- Engineering reviewed drawings and documentation for components
Validate
To validate the new process, pilot components were transferred using the revised process. The team quickly realized they hadn’t considered the differences in customs requirements between the different countries. Revisions to the original design were made.
The new process worked well, and the company was able to improve its business results and local market competitiveness by 19% using this new sourcing strategy.
Best Practices When Thinking About DMADV
This is a major team activity, so keep some of these things in mind.
Engagement
At the beginning, identify who should be on the team, both the core team as well as the extended team. Most DMADV projects require the engagement of a wide array of functions.
Understand the Customer Requirements
Since you are starting from scratch, take the opportunity to fully understand what the customer needs and how you will be able to measure the key metrics or CTQs.
Break the Project into Manageable Pieces
Given the intensity of the method, allow some time for the team to absorb and internalize all the activities and outcomes of the process. There will be serious diminishing returns if meetings are too frequent or too long.
Other Useful Tools and Concepts
While we’ve discussed DMADV at length, that isn’t the only tool at your disposal. Learning how to utilize Cpk is one of the core calculations you’ll encounter in your data analysis. As such you owe it to yourself to see how this calculation impacts your productions as a whole
Additionally, learning how to create a Corrective Action Report is one of the most useful ways to account for defects in your processes. If this is a new concept, then you owe it to yourself to look into how to create the document in your organization.
Conclusion
The steps of DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Validate) are used to improve a product or process when the current process cannot be incrementally improved to a level that will satisfy customer requirements, or when there is no existing product or process.