
Key Points
- Bartlett’s test is used to check homogeneity within variances.
- It can be thought of as a 1-way ANOVA.
- It makes use of a null hypothesis assuming that all variances are equal when comparing data sets.
The Bartlett Test is named after the English statistician, Maurice Stevenson Bartlett. The test is also known as the Bartlett’s test for homogeneity of variances. It is most used in doing a 1-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA).
ANOVA is used to determine whether there is any statistical difference between the means of three or more groups of continuous data. There are two underlying assumptions for ANOVA. One is that all data groups need to be normally distributed, and the other, is that the variances need to be statistically equal.
Overview
You will use the Bartlett Test to determine if the variances of your data sets are equal when your data is determined to be normally distributed. A similar test, the Levene’s Test is better suited when your data is not normally distributed. The Levene test is less sensitive than the Bartlett test to depart from normality. If you have strong evidence that your data comes from a normal, or nearly normal, distribution, then Bartlett’s test has better performance.
The null hypothesis (Ho) for the Bartlett Test is that all variances are equal. The alternative hypothesis (Ha) is that at least one of your variances is different. The test statistic for the Bartlett Test is:
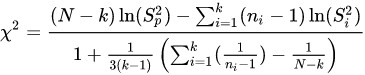
Best Uses of the Bartlett Test
Typically, you’re not going to use a Bartlett Test for the likes of non-normal data sets. As mentioned, the Levene test is a better overall fit for non-normal data. However, where the Bartlett Test shines is in the use of data sets where there aren’t any major departures from a normal distribution. As such, you’ll need to do a check before making use of this test in your statistical analysis.
An Industry Example
The Six Sigma Black Belt wanted to know whether the average run speed of the company’s three manufacturing machines was equal. She gathered some sample data and used ANOVA to answer her question. She used a statistical software package and determined that the three sample data sets were all normally distributed. She then ran the Bartlett Test to determine whether the three variances were equal. Below is the output of her analysis:
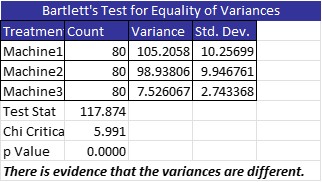
As you can see, the variances are not equal, therefore it would not be appropriate to use the standard ANOVA. Instead, you can use Welch’s ANOVA which does not require equal variances.
Other Useful Tools and Concepts
Looking for some extra tools to get you going? You might want to learn about the differences between a subject matter expert and a consultant. Both types of professionals are going to be integral in your organization, but they serve different roles when approaching any project.
Further, you might need to learn all about project ROI. This approach allows you to selectively pick projects in need of investment and resources by looking at how the return on your investment shakes out.