
Key Points
- B10 is a metric for measuring reliability in a deliverable.
- While it was originally used for manufacturing it applies to many industries.
- Proper utilization allows you to correctly gauge just how reliable a product is, but it is a costly and time-consuming process.
Giving customers confidence in the reliability of your products whilst meeting their expectations for service life and warranty is a surefire way to build customer loyalty and satisfaction. As such, using B10 Life, we have a simple and effective metric to communicate the reliability of our products. Let’s find out more.
Overview: What Is B10 Life?
The B10 life metric originated with ball and roller bearing manufacturers and has since become widely used across a variety of industries. The B10, or Bearing life, nomenclature refers to the point at which 10% of units in a population will fail.
Alternatively, you can regard it as the 90% reliability of a population at a specific point in its lifetime. The B10 life metric gained traction among ball and roller bearing manufacturers due to the industry’s requirement that no more than 10% of bearings in a given batch should fail due to fatigue by a specific time.
The metric is often quoted as a time, a distance, or several actuation cycles. It comes to which is appropriate for the product and its application. Examples could be:
- an electric motor may have a B10 life of 3000 hours
- a heavy-duty truck may have a B10 life of 1 million miles
- a pneumatic valve may have a B10 life of 500,000 actuation cycles
The calculation is typically performed by statistical interpretation of test data. Additionally, this is most commonly done by Weibull analysis. It is represented in a graphical plot as shown in the example below.
A thorough understanding of failure modes, in particular design failure mode and effect analysis, and root cause analysis is advisable to interpret the test data used to derive this metric.
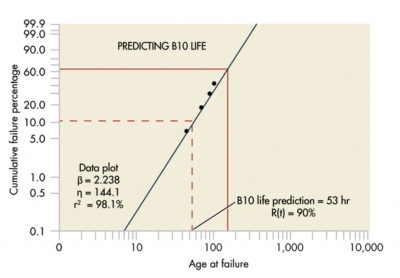
Image source: www.machinedesign.com.
2 Pros and 1 Con of B10 Life
Like many reliability and failure rate metrics, there are benefits and drawbacks to be aware of when calculating B10 life. With this in mind, let’s explore some of these in more detail.
Pro: It’s a Known and Used Industry Reliability Metric
Originating in the bearing industry and now widely adopted across most industrial sectors. The use of B10 Life allows consumers the ability to review, compare, and interpret reliability data with relative ease.
Pro: You Can Use It to Set Your Warranty Period
All companies strive to reduce their costs from warranty claims and improve customer satisfaction by delivering good product reliability. Knowledge of when a product will fail and a statistical analysis of the percentage of products that will fail in a given lifetime is hugely valuable. As such, this comes in handy when setting a realistic warranty period.
Con: Testing to Failure Can Be Costly and Time-consuming
Even though we may use a statistical approach to help cut down on sample size, we still need to evaluate products by testing for failure. However, this could be testing millions of actuation cycles, thousands of hours in service, or miles covered. All of this can be time-consuming and costly.
Why Is B10 Life Important to Understand?

By calculating and understanding B10 life, we can develop competitive products that are optimized for their application and meet customer requirements.
It Gives Customers a Clear Indication of Product Reliability
Whether it’s a domestic light bulb or a piece of construction equipment, the B10 life metric allows the customer to make an informed decision. This decision hinges on the suitability of the product to their application and requirements.
It Helps Us Develop a Robust Maintenance and Service Strategy
Often, the B10 life is set as a requirement during product creation and development. It is developed from a critical-to-customer (CTC) flowdown. This allows us to develop a robust maintenance and service strategy, in parallel with product development. In turn, this supports the B10 life requirement.
It Helps Us Balance the Function and Cost Equation
Setting such a requirement early in product creation and development allows us to make important decisions and trade-offs on both product function and cost to avoid over-engineering. Further, verification of B10 life can provide an opportunity to rebalance product function and cost. As such, this is a strategy often deployed in the automotive industry after launch and during the product lifespan.
An Industry Example of B10 Life
An industrial engine manufacturer had an opportunity to enter a new market sector and make its product available for stationary power generation. Two of the key requirements for stationary power generation engines are running hours without failure and product reliability. B10 life is a common metric used to assess and compare engine suitability and performance in the sector.
The metric was evaluated for the existing engine in the new stationary power application. As the engine would not travel any physical distance, the existing metric was changed from mileage to run hours. In addition, a new duty cycle was derived for the physical testing, taking into account the specific engine speed and load running conditions.
Following an intensive test phase, engine run time data was interpreted using a Weibull analysis. Afterward, a new B10 life was calculated. The warranty period and service and maintenance strategy were updated to reflect the newly calculated B10 life. Subsequently, the engine was successfully launched for the stationary power generation market.
Why It Matters
Your organization is only as good as the end product you’re producing. If you’re sticking to your guns and working within the data-driven paradigm of Six Sigma, then you surely understand the importance of having actionable data. B10 Life is just one other measurement to guarantee the best possible product you can produce.
Best Practices When Thinking About B10 Life

As with many failure rate and reliability metrics, there are some key points to consider when calculating B10 life. Let’s explore three of these.
Measure and Report the Correct Metrics
When we think about the life of a product or component, we can measure and report a variety of different metrics. These metrics could be service hours, mileage completed, number of cycles, or others, and careful consideration should be applied to what is measured and reported.
Data Integrity Underpins Your Calculations
Customers and consumers make important decisions based on quoted failure rates. Reliability calculations and failure rate analysis are dependent upon conducting the right tests across a suitable sample size and measuring and capturing the right data.
Accelerated Testing Needs Confidence in Correlation
Often, the time to failure can be many thousands of hours, or millions of actuation cycles, which is both costly and time-consuming to replicate. Accelerated testing, where the test parameters are deliberately made more severe, is one way to reduce the burden of cost and time. However, this requires confidence in the correlation to real-world customer usage and duty cycles.
Other Useful Tools and Concepts
We’ve talked a fair bit about reliability today. However, if you want to see how quality shapes customer expectations, I recommend reading up on House of Quality. This approach is a time-consuming and costly endeavor but yields fantastic results when you get it up and running.
Further, you might want to understand the rate of defects when production is underway. Being able to calculate DPMO, or defects per million opportunities is a life-saver. This calculation is one of the cornerstones of Six Sigma and is a must-know for anyone doing analysis.
A Final Thought to Consider
Reliability analysis and determination of metrics such as B10 life can be the key differentiator when customers are making investment decisions. However, taking the time to understand and calculate this metric can bring the competitive advantage you need to secure the deal.